Monitoring patient oxygenation levels in intensive care is key, but prematurely born babies pose a unique problem. “They are very vulnerable, since their organs are immature, in particular the brain and the lungs,” says Emilie Krite Svanberg, who specializes in anesthesiology and intensive care medicine at Lund University. “Prematurely born children weighing as little as 500 grams very frequently have respiratory distress syndrome and need strong surveillance – unfortunately, this often demands repeated X-ray recordings.” The main aim of Krite Svanberg’s work is to reduce the use of damaging X-rays by using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for 24-hour non-invasive monitoring of lung tissue oxygenation.
Oxygenation is often measured by blood gas analysis but optical techniques, such as common pulse oximetry (with a clip around the index finger), are also routinely employed. NIRS is still an emerging technique. “Using broad-band spectroscopy it is possible to distinguish between oxygenated blood and non-oxygenated blood. My first studies related to refining such techniques, for example, by working with a time-resolved spectroscopic variety of NIRS, which is less sensitive to the strong light scattering in tissue,” says Krite Svanberg. But other spectroscopic developments from the physicists in the engineering faculty at Lund University were emerging, including narrow-band spectroscopy using tunable diode lasers. “They had already applied the GASMAS (gas in scattering media absorption spectroscopy) technique to construction materials, pharmaceutical preparations, and also for diagnosis of sinusitis,” Krite Svanberg explains. “The idea emerged to apply these techniques to newborn children, who are small enough to yield a useful optical signal from their lungs.” How does the technique work? Weak laser light is fiber-optically ‘injected’ into the body, and scattered light, which has partly passed through air-containing tissues, reaches the body surface, where it is collected by a detector. Two narrow-band diode lasers are employed and scanned through sharp molecular absorption lines – one through an appropriate oxygen line, and one through a water-vapor line. “The latter is employed for normalization purposes, since the concentration of water vapor is determined by the temperature only, which is known,” says Krite Svanberg. “The problem with unknown optical path length through the scattering medium can then be largely eliminated to yield calibrated oxygen gas levels.”
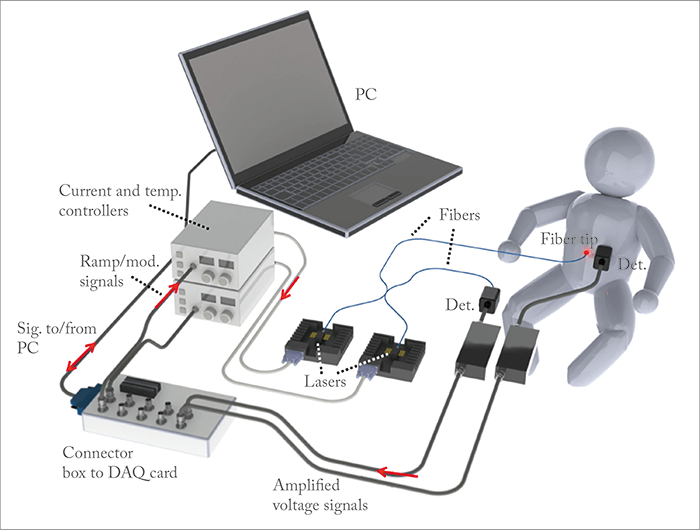
In the initial clinical trial (1), clear oxygen and water vapor signals were detected from the chests of a large number of full-term newborn children. There are still issues to be resolved, however. “We have had signal intensity and normalization problems, which we expect to be solved with improved equipment and measurement approaches. This is important before proceeding to studies of premature children.” The next stage? “We need specially designed laser sources and optical arrangements to obtain clinically adapted equipment for routine application,” say Krite Svanberg. The project has received EU funding, and will continue in collaboration with three other enterprises (in Sweden, Norway and Germany) and the interdisciplinary research group at Lund University. Krite Svanberg believes the findings so far show great possibilities: “With a new proposal to deliver the light internally in the patient via the endotracheal tube of the respirator – which is frequently already there for the severely ill patients – it might even be possible to extend the technique to adult monitoring.”
References
- E Krite Svanberg et al, “Noninvasive monitoring of oxygen in the lungs of newborn infants by diode laser spectroscopy”, Pediatr Res (2015). DOI: 10.1038/pr.2015.267
